
Gardening enthusiasts often find raised garden beds to be a delightful and productive way to grow vegetables. These beds offer numerous advantages, including better drainage, easier access, and more control over soil quality. If you’re looking to start a vegetable garden in a raised bed, here’s a step-by-step guide to get you started.
Step 1: Choosing the Right Location
Your raised bed should be placed in an area that gets at least six to eight hours of sunlight daily. Ensure the location is away from large trees and shrubs that could compete for nutrients and water. Also, consider accessibility for watering and maintaining your garden.
Step 2: Selecting Your Raised Bed
Raised garden beds come in various materials like wood, stone, or metal. Wooden beds are popular but ensure the wood is untreated to avoid chemicals leaching into the soil. The bed should be at least 12 inches deep to accommodate the roots of most vegetables.

Step 3: Preparing the Soil
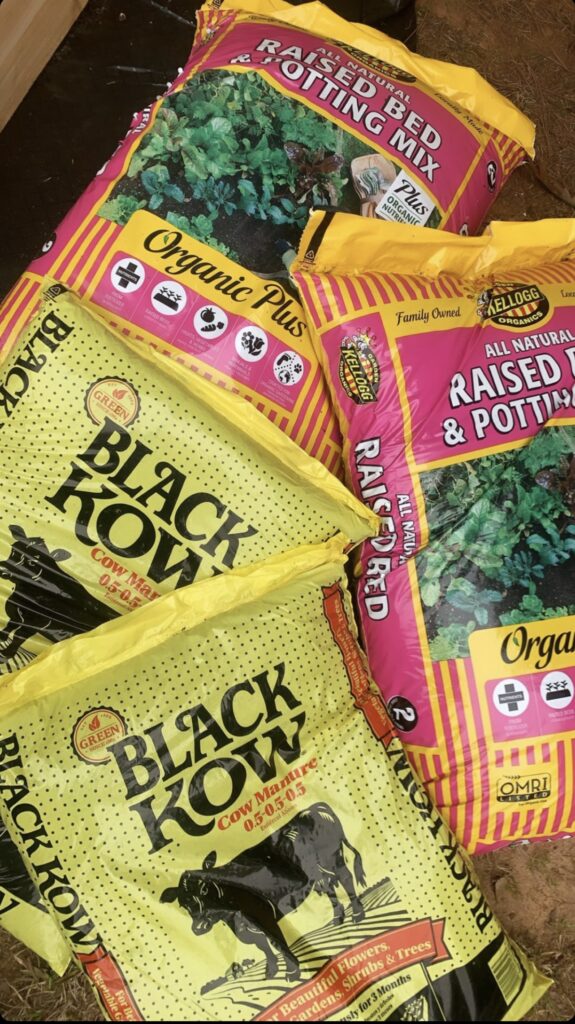

A mix of topsoil, compost, and other organic matter is ideal for raised bed gardening. This blend provides nutrients and improves soil drainage and aeration. Fill your bed with this mix, leaving a couple of inches from the top for mulching later.
Step 4: Choosing Your Vegetables
Select vegetables that you enjoy and are suitable for your climate. Consider the spacing needs of each plant, as overcrowded plants can lead to poor growth and disease. Some easy-to-grow options include lettuce, tomatoes, peppers, carrots, and radishes.
Step 5: Planting
Follow the instructions on your seed packets or seedling containers for planting depth and spacing. Some vegetables like carrots or radishes are best grown from seeds sown directly into the soil, while others like tomatoes and peppers may be easier to start with seedlings.

Step 6: Watering and Maintenance
Raised beds may require more frequent watering as they drain better than in-ground beds. Ensure your plants receive an inch of water per week, either through rainfall or manual watering. Regularly check for weeds and pests, and consider organic options for pest control and fertilization.
Step 7: Mulching and Soil Health
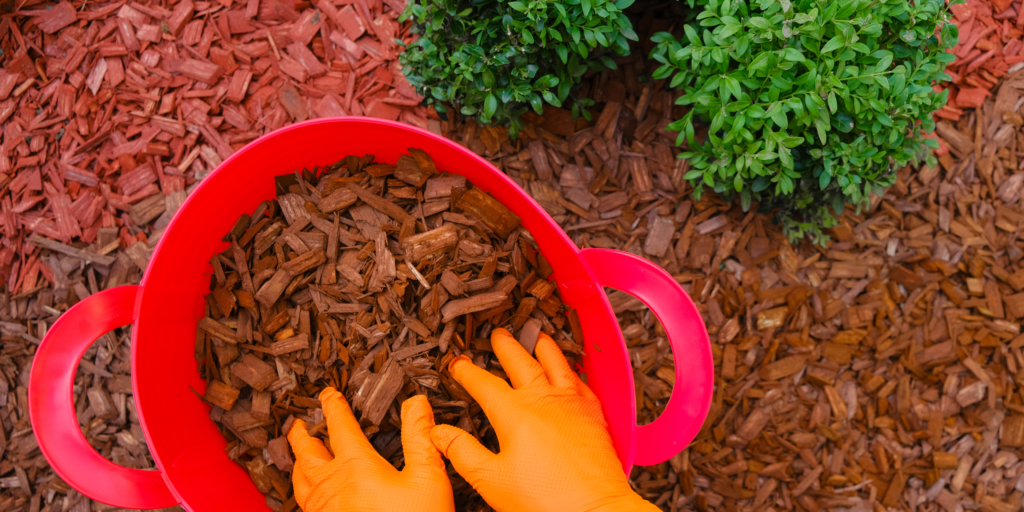

Mulch helps retain moisture, suppress weeds, and keep the soil temperature stable. Organic mulches like straw or shredded leaves also add nutrients to the soil as they decompose. Each season, rejuvenate your soil by adding fresh compost or organic matter.
Growing vegetables in a raised garden bed can be a rewarding and efficient way to garden. With the right location, good soil, proper plant selection, and regular maintenance, your raised bed can yield a bountiful harvest. Remember, gardening is a learning process, so don’t be afraid to experiment and see what works best in your garden.
Ready to transform your gardening experience and enjoy a plentiful harvest? Dive into our comprehensive guide on raised bed vegetable gardening. Click to learn more, start your own raised garden bed, and join a community of enthusiastic gardeners! Don’t forget to share your progress and success stories with us. Let’s grow together – your journey to a thriving vegetable garden starts here!
Happy Gardening!









Leave a Reply